Source: news.google.com
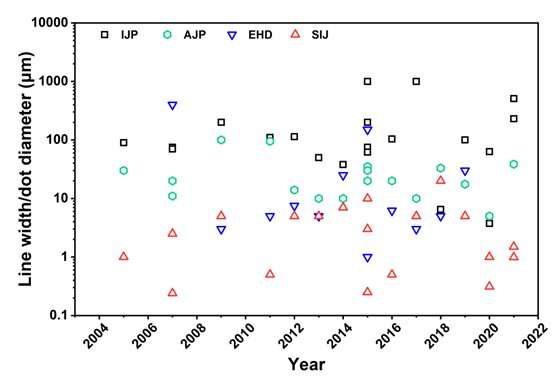
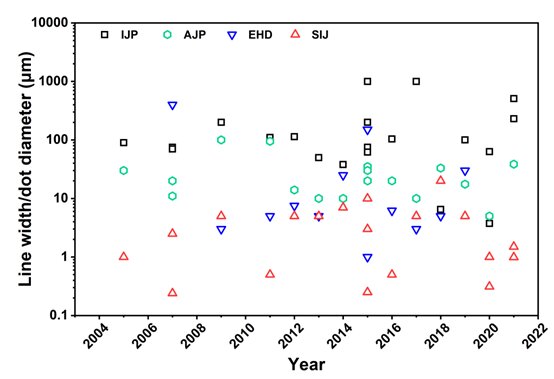
Fig. 1 Layout of lines produced by inkjet printing of various solutions. Credit: Compuscript Ltd.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, image recognition and 5G communication technology, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies are developing at an alarming rate. In the context of COVID-19, remote office and consumer interaction is increasing. The market turns its attention back to AR/VR and increases its investment in technological applications.
One of the main reasons for the burst in the market is the advancement of new display technology with excellent performance. As a staple of AR/VR, display devices must have ultra-high pixel density and fast refresh rate, as well as small and lightweight bulk. At present, liquid crystal display (LCD) and organic light-emitting diode (OLED), two main display technologies, have been applied to near-eye displays (NEDs) and head-mounted displays (HMDs). ). However, due to low conversion efficiency and color saturation, rapid aging, and short service life, the development of new display technologies has accelerated.
Micro-LED has excellent optical performance and long life, which is considered the next generation and latest display technology. The minimum pixel size reaches tens of microns and the high pixel density makes it suitable for AR/VR. In addition to high pixel density, full color is also the key element to realize Micro-LED in AR/VR, and the color conversion scheme is an effective method. Quantum dots were deposited on blue or ultraviolet micro-LED chips using inkjet printing technology to achieve three-color luminescence and avoid mass transfer technology. In recent years, inkjet printing technology shows great potential in micro-manufacturing due to its advantages of digitization, pattern creation, additive manufacturing, low material waste, and large-area printing. In particular, the rise of super inkjet (SIJ) printing technology can achieve ultra-high-resolution printing with minimal printing line width in the submicron region. It sheds light on manufacturing a high-resolution color conversion layer for micro-LEDs for full-color display, and in particular for augmented/virtual realities (AR/VR).
The authors of this article published in Optoelectronic advances overview of the principle of inkjet printing technique and its application in micro displays for AR/VR. In this review, the progress of AR/VR technologies is presented first, followed by discussion of the adaptability of micro-LED display technology in AR/VR and the advantage of printing a color conversion layer for micro-LEDs. using inkjet printing technology. The mechanism of energy transfer without radiation and the influence of color conversion layer thickness on color conversion efficiency are discussed. The advantages of SIJ over other resolution printing technologies are presented.
In the second part, the printing principle of various inkjet printing technologies was presented, as well as two key issues: optimization of ink rheological parameters and reduction of coffee ring effects. The rheological parameters of the ink suitable for each printing technology and the influence of the rheological parameters on the printing effect were introduced. Two solutions to the caffeine ring effect and specific enhancement methods were reviewed. Finally, some potential problems associated with the color conversion layer are highlighted, including light crosstalk, blue light absorption, and self-absorption effect. This review article serves as a reference for the areas of inkjet printing technologies, micro-LED full colorization, and its application in AR/VR.
-
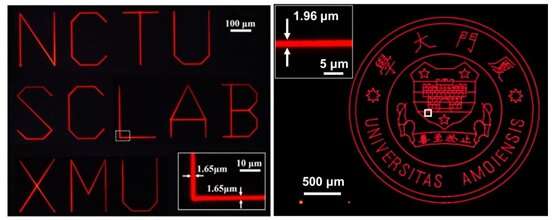
Fig. 2 XMU lettering and emblem printed by SIJ. Credit: Compuscript Ltd.
-
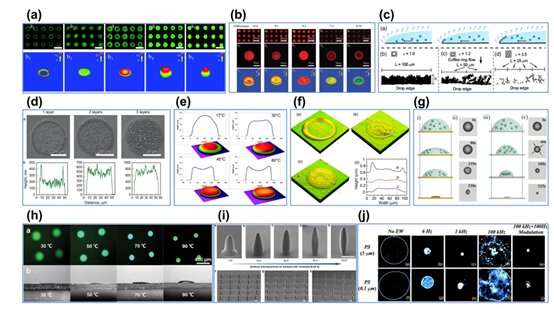
Fig. 3 Investigation on the suppression of the coffee ring effect. Credit: Compuscript Ltd.
More information:
Xiao Yang et al, An overview of the principle of inkjet printing technique and its application in microdisplays for virtual/augmented realities, Optoelectronic advances (2022). DOI: 10.29026/oea.2022.210123
Provided by Compuscript Ltd
Citation: The Principle of Inkjet Printing and Its Applications to AR/VR Microdisplays (2022, June 30) Retrieved December 1, 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-06-principle-inkjet -applications-arvr-micro-screens.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.
Read More at news.google.com