Source: news.google.com
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are becoming more common in the aerospace industry. The technology is being implemented in training, maintenance, and design and manufacturing.
A survey commissioned in July by Grid Raster indicated that 42% of respondents plan to implement AR/VR technologies within the next 12 months. Another 51% are investigating uses for AR and VR in their operations. Grid Raster is a company that provides cloud-based XR platforms to support AR/VR/MR (machine learning) on mobile devices.
How AR and VR are used in the aerospace industry
The implementation of AR and VR to support design and manufacturing is one of the uses of the technology in the aerospace industry. “You have to put tons of cables on planes and spacecraft. Traditionally, it has been done manually,” said Rishi Ranjan, CEO of Grid Raster. design news. “With AR, you can set up cables virtually, a process that saves weeks.”
People are also using AR and VR in manufacturing and design to show workers how apps are supposed to work. Workers can learn their jobs in a completely virtual world before they start running the manufacturing process.

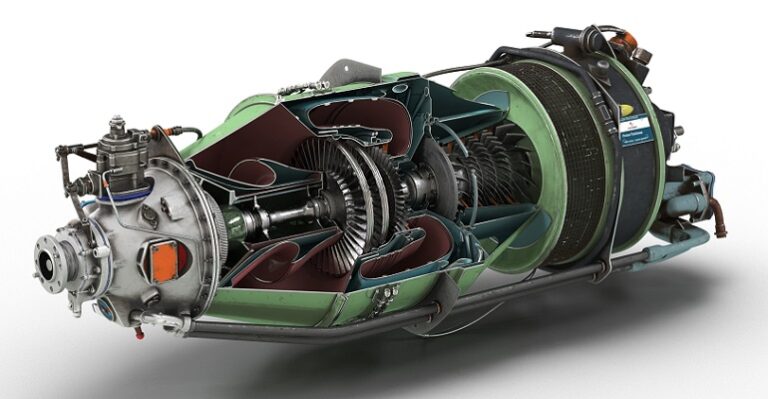
Aerospace companies are using virtual reality in the jet engine manufacturing process.
AR and VR technology is also being used for repair and maintenance in the aerospace industry. “The goal is to make sure the team is in the air most of the time,” Ranjan said. “If you’re using AR for maintenance, you get the visual image on the screen of the work you need to complete. You don’t have to go to a manual or a video. That puts the machine in the air faster.”
Training is another common use of AR and VR, whether for flight instruction or repair. “AR and VR can be used to develop muscle memory. Manual training is expensive. With AR and VR, you can do the training less expensively,” Ranjan said. “AR and VR companies are building simulators that can be deployed remotely as long as you have a screen. Students do not need to go to a certain place. For some of the really dangerous training, the students don’t have to risk the plane.”
The Grid Raster study revealed that aerospace companies are leveraging AR and VR technologies in the AR-assisted workforce on production lines (83%); customer visits and AR assisted maintenance (75%); employee training programs (53%); and AR-Assisted Design Processes for Aerospace Engineers (30%).
COVID-19 has increased the use of AR and VR
According to Ranjan, the use of AR and VR in the aerospace industry has grown during the pandemic. “COVID-19 has had an impact on aerospace executives, prompting AR and VR deployments,” Ranjan said. “Twenty-eight percent of those executives said that COVID-19 weighed heavily on their decision to accelerate this technology. Another 39% indicated that they started the adoption process as a result of the pandemic.”
The very nature of AR and VR lends itself to remote access. “Much of the use of AR and VR is due to employees not being able to go to offices. You can easily go virtual from home,” said Ranjan. “You can keep practicing and learning muscle memory. People can do it at home, and when they go back to the office, they will be more efficient.”
Ranjan noted that aerospace decision makers are turning to AR and VR for their efficiency. “Aerospace companies that have done AR and VR implementations are seeing various results,” Ranjan said. “Most respondents said they are achieving a 15% to 20% increase in efficiency and a 5% to 10% increase in overall cost savings.”
The uses of AR and VR in the aerospace industry tend to be quite different. “If you look at a common application in the aerospace industry, let’s say training, virtual reality is used 90% of the time,” Ranjan said. “If you’re working on making the aircraft, you’re using AR. To explore maintenance issues, it’s VR, but to fix the planes, AR is being used.”
How does cloud technology influence AR and VR?
Ranjan noted that the ability to leverage AR and VR through cloud technology is important in the aerospace industry. “51% of aerospace executives are concerned about the need to move their current AR/VR solutions to a cloud-based environment,” said Ranjan.
Using AR and VR requires considerable computing power. Connecting to a cloud system is one way for users to get the level of computing they need. “If you look at AR and VR, you’re rendering the camera in real time in AR and VR,” Ranjan said. “You have to do a lot of computing. The aerospace industry has a minimum of computation at hand.”
He also noted that the use of cloud connectivity in AR and VR is expected to increase, as devices will need to become increasingly lightweight. “If you bring the information with the processing you need, it’s in the cloud,” Ranjan said. “If you use the cloud as your renderer, you can do better alignment and the camera will know what it’s looking at. “
Cloud-based AR and VR can also be scaled more easily than in-house systems. “We are finding that the benefits of AR and VR are achieved more quickly when manufacturers ensure they have implemented the solutions in a cloud-based environment,” said Ranjan. “Cloud-based systems can provide greater functionality and scalability.”
Rob Spiegel has covered automation and control for 19 years, 17 of them for design news. Other topics he has covered include supply chain technology, alternative energy, and cybersecurity. For 10 years, he was the owner and editor of the gastronomic magazine Chile Chile.
Read More at news.google.com
